Future-focused learning not only equips students with the skills and abilities to succeed in a fast-changing, interconnected world, but also empowers them to take charge of their own learning journey. This approach sparks their interest and involvement in learning, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility. In these environments, students collaborate with peers, mentors, and teachers, using critical and creative thinking to tackle challenging problems and gain a global perspective. Education systems are discovering methods to prepare a diverse workforce focusing on 21st-century learning and teaching. The 21st-century workforce requires workers capable of complex problem-solving in global systems. Casey and Worthen (2019) suggest that students must be prepared to navigate a globalized workforce through “complex outcomes like systems thinking, applied problem-solving, social and collaborative skills, and civic and social awareness.”
Operation Xcel is a prime example of an educational initiative that prepares students for future success through a multifaceted approach. It focuses on leadership development, career mindfulness, and most importantly, STEAM education. STEAM, an acronym for Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics, is a comprehensive educational approach that engages students through intriguing lessons that integrate various subjects, encourage questioning, and promote project-based learning. This approach enables students to apply their existing knowledge, acquire new skills, and develop critical thinking abilities in a real-world context, preparing them for future careers that will demand STEAM skills.
Creative thinking is a cornerstone of the education system's mission to prepare students for the future. Yet, it is often overlooked due to a lack of consensus on its definition and ineffective teaching methods. Creative thinking, a higher-order skill, is transformative in almost every aspect of life and drives economies. Skills like 'exploration and improving' and brainstorming, identified by Rosen, Simmering, and Stoeffler (2020), are theoretical concepts and practical tools for students to learn, develop, and demonstrate. By equipping students with creative thinking skills, we empower them to generate innovative ideas, solve complex problems, and create tangible solutions, enhancing their ability to apply these skills in real-life situations.
Operation Xcel teachers design lesson plans that incorporate real-life learning, such as activities related to money management and starting a business. This includes games emphasizing business skills, math reflecting real-life situations, and reading and comprehension materials about issues that students may encounter one day. Educators who champion future-focused learning are not just teachers, but facilitators of knowledge and understanding. They recognize and cater to their students' unique needs and strengths, demonstrating adaptability by employing a diverse range of effective teaching methods. By creating an environment that encourages and empowers students to take control of their learning, these educators are shaping the future of education.
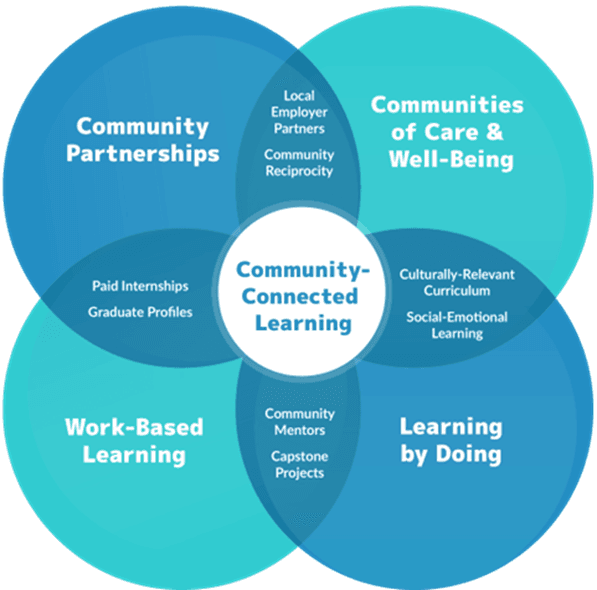
Future-focused Education (FFE, 2024) is an organization that started in New Mexico to meet the needs and aspirations of underserved youth trapped in a one-size-fits-all education model. FFE adopted a four-pillar model that includes community partnerships, communities of care and well-being, work-based learning, and learning by doing. The model reflects the interconnectivity and positive impact of employer partnerships, community reciprocity, internships, graduate profiles, community mentors, capstone projects, culturally relevant curriculum, and social-emotional learning (SEL). (See Attached Picture – Four Pillar Model).
Operation Xcel incorporates SEL in all its programs because it recognizes that educational programs must meet the children where they are instead of vice versa. This means that each child brings the culture of their community with them to academic settings. It is up to the education systems, including academic enrichment programs such as Operation Xcel, to create a safe place where children are intellectually and emotionally stimulated through a holistic approach. For example, two of the Operation Xcel sites report that they sponsor a weekly SEL day when teachers intentionally pair up with students to “reflect on and unpack their day.” Students can create and set out to achieve personal goals with measured progress. Teachers learn more about each student and redesign their “interactive strategies,” enhance service delivery, strengthen relationships, create a supportive space, and ensure they meet the students' needs. The success of the SEL programs at Operation Xcel has been measured by how well the students are equipped to manage their emotions, empathize, make responsible decisions, and acquire positive relationship-building skills. SEL programming is future-focused in that the students learn skills that, once grasped, are for their success in school, life-long leadership, and character development. This project-based learning is crucial in a fast-paced global economy where students will work at some point.
Community partnerships prove that youth can lead when involved in essential community experiences as future change agents. There is a reciprocal advantage when communities engage in education programs as mentors and presenters. Community partners are more connected to the people they serve when they share with students and impact their curriculum. Operation Xcel hosts community partners that help students learn about various subjects, including drug abuse prevention, managing mental illness, and many other topics. Some of these programs are non-profit programs that are federally funded suggesting that their ability to obtain funding is based upon the student population that needs their services. Underserved youth, some from disadvantaged communities, are the most vulnerable to experiencing various societal issues from which they need to mentally escape to have a rational and healthy mindset. It is through its community partners, college student volunteers, corporate volunteers, and other community members that Operation Xcel can depend on to assist in the successful and holistic development of its students. Students benefit by acquiring knowledge and new skills, helping foster leadership potential in their current and future settings.
As the students learn to solve problems independently using their progressive skill acquisition, they are more apt to solve other complex problems using the same skills having learned by doing them. Preparing students for future leaders in a global economy requires more than teaching them to pass a test. Future-focused learning requires that students acquire problem-solving skills and continue to cast them into necessary tools and skills for critical thinking to solve global issues where they will, one day, attain profitable careers as future leaders, should they choose.
References:
Casey, K., & Worthen, M. (2019). Developing a modern teacher workforce: federal policy recommendations for professional learning and supporting future- focused, competency-based education systems. Vienna, VA: iNACOL.
Future Focused Education (2024, February 29). Future FocusED Education: The best education for the students who need it most. https://futurefocusededucation.org/about/#next
Rosen, Y., Simmering, V., Stoeffler, K. (2020). Imagine: Design for creative thinking, learning, and assessments in schools. The Journal of Intelligence, 8 (16), 1-20.

